ibaa
General information
IBAA pharmaceutical Factory (IPF) is a Private Limited Company. It is the first plant of sterile cephalosporin products in the country and region with standards that meet the requirements of National Medicines and Poisons Board (Sudan) NMPB, International Conference on Harmonization (ICH), and World Health Organization (WHO). IBAA Pharmaceutical Factory is equipped with a one production lines capable of producing cephalosporin sterile injectable dosage forms to satisfy the needs of our market for human use. IPF has its Pharmaceutical Formulations Manufacturing Plant and its head office at Kafori, Khartoum, which is 13 km from Khartoum international Airport, from where all the key functions such as Manufacturing, Testing, Production planning, Finance and Distribution are controlled. There are no hazardous manufacturing units in the vicinity of the company. The plant manufactures products under National Medicines and Poisons Board(Sudan) under a manufacturing license.

Facilities & capacities:
The plant is surrounded by a well-maintained lush green garden. The plant has easy access to public transport and cargo transportation. It has a built up area of 2400 Sq. Meters. – As per the full capacity, the production reach to 40,000,000 vials per annum).
Quality management system (QMS):
IBAA Pharmaceutical Factory, has been comprehensively designed to account for each step of the process of manufacture and analysis of the pharmaceutical product. The system is aimed at accomplishing the quality objectives those in line with the firm quality policy as expressed by management.
The QMS of Ibaa Pharmaceutical Factory is based on the ISO 9001 and WHO GMP requirements. The system refers to other international guidelines like the Eudralex, PIC/S and ICH for guidance.
Quality assurance department is directly responsible of the QMS. The QMS encompass all departments and departments within the organization hence each department shares the responsibility of maintaining the QMS. Linkage and interrelationships between different parts of the system is considered in the way the system is designed based on general Quality assurance procedures, departments/ departments master SOPs -SOPs that organize the major activities of each department or department- and the work instructions for performing each job or task.
Organogram:
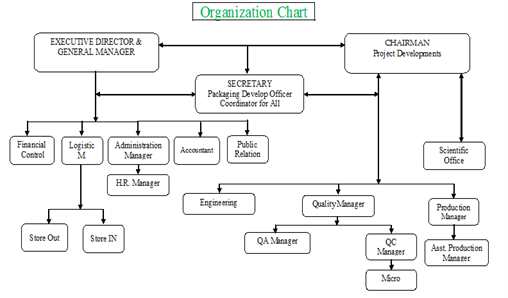
Key personnel
Name: Dr Khalid Ibrahim Ali
Designation: Chairman
Experience: 25 years in manufacture of pharmaceutical Products.
Responsibilities: To ensure that products are produced and stored according to the appropriate documentation in order to obtain the required quality, to approve the instructions relating to production operations, including the in-process controls, and to ensure their strict implementation, to ensure that the production records are evaluated and signed by a designation person, to check the maintenance of the department, premises, and equipment, to ensure that the appropriate process validations and calibrations of control equipment are preformed and recorded and the reports made available, to ensure that the required initial and continuing training of production personnel is carried out and adopted according to need, Authorization of written procedures and other documents, including amendments, plant hygiene, approval and monitoring of contract manufacturers, designation and monitoring of storage conditions for materials and products and monitoring of compliance with GMP requirements.
Collaborations:
IBAA pharmaceutical Factory and Sudanese universities have mutual collaborations regarding training, chemical analysis for some materials, as well as calibration of instruments.
Community interactions & achievements:
IPF usually interact to its community which is the direct target of its care. It always respond to their needs in form of drugs and monetary donations in cases of national crises, health caravans.Moreover, IPFsupports the national medical associations those are held annually to increase the knowledge and skills of junior physicians and students where the practice experiences are shared
- Product launches
IPF is keen to launch their products to attract the awareness of national physicians and pharmacists. These launches discuss the quality issues, advantages, and potentialities of the launched products. This increases the openness of physicians and pharmacists to the nationally produced drugs, which has great benefits to our country
- Departments:
- Production
It is an independent department that assume the production. It is responsible for Manufacturing, Timely delivery of products, Raw material planning, and Production planning
-
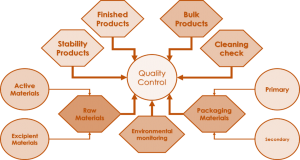
- Quality control
The QC department is responsible of product and material analysis, release, and sampling including raw material, packaging material and water sampling and analysis (purified and WFI), Stability study, environmental monitoring including swaps, plates, and fingerprint, verification of cleaning samples including swaps and rinse and participation in process and cleaning validation. Tests carried within the QC department ranges from physical, chemical to microbiological tests. The British and United States Pharmacopoeias are the main references in the Quality Control Department for analysis. New analytical methods are also developed and validated for non-pharmacopeial methods. The chart below shows the activities of testing within the Q
Quality assurance
It is independent of production and quality control departments and has the responsibility and authority to:
- Validate manufacturing controls, equipment, procedures, analytical procedures, analytical equipment, SOP’s and ensure cGMP compliance through periodic self -inspection.
- Evaluate batch records before final disposition of the batch.
- Lay out a training program schedule for all departments and carry out initial and continuous training of departmental personnel.
- Prepare SOP’s, MFR’s (Master Formula Cards), Quality manual, Training manual, Testing/Validation Protocols etc.
- c-GMP administration of the entire plant.
- Vendor Audits.
Research & development:
This department is responsible for:
- Developing the new product formulation.
- Establish in-process and finished product specifications
- Stability studies
- Scale up and documentation
- Technology transfer
- Troubleshooting the emerging issues regarding the product formula.
Engineering:
This department is responsible for:
- Regular maintenance of machines in the different departments and changing the spare parts.
- Supervising the setup of new production lines& instruments.
Marketing & distribution:
This department is composed of a manager, field supervisors, training & promotion supervisor, and medical representatives. It assumes the following:
- Promotion of the drug products in hospitals, physician clinics, and community pharmacies.
- Making the market analysis for potential drug products to be developed
- Cooperating with the R&D department in formulation development
- Supervising the distribution and sales agencies of the products.
Store department:
This department involves:
- Raw materials store
- Packaging materials stores
- Finished goods store
Purchasing department:
This department supervises the supplies purchasing of different logistics needed by different departments based on the foreseen needs through the year work plan
Risk management department
This department assume the following roles:
1.Designing and implementing an overall risk management process for the organization, which includes an analysis of the financial impact on the company when risks occur
2.Analyzing current risks and identifying potential risks that are affecting the company
3.Performing a risk evaluation: Evaluating the company’s previous handling of risks, and comparing potential risks with criteria set out by the company such as costs and legal requirements
4.Establishing the level of risk the company are willing to take
5.Preparing risk management and insurance budgets
6.Risk reporting tailored to the relevant audience. (Educating the board of directors about the most significant risks to the business; ensuring business heads understand the risks that might affect their departments; ensuring individuals understand their own accountability for individual risks)
7.Explaining the external risk posed by corporate governance to stakeholders
8.Creating business continuity plans to limit risks
9.Implementing health and safety measures, and purchasing insurance
10. Conducting policy and compliance audits, which will include liaising with internal and external auditors
11. Maintaining records of insurance policies and claims
12. Reviewing any new major contracts or internal business proposals
13. Building risk awareness amongst staff by providing support and training within the company)
IBAA
The only pioneer of manufacturing sterile cephalosporin’s antibiotics in Sudan and region
Quick Links
Get In Touch
- Email: info@ibaamedical.com
- Phone: +249912392324
